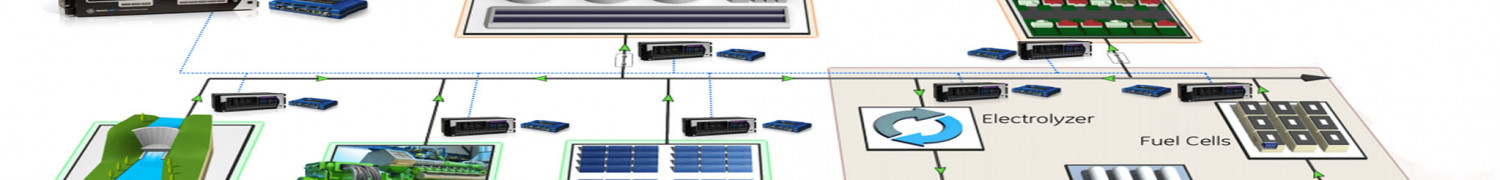
A microgrid is an integrated energy system with local Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) such as local loads, generating assets and possibly energy
storage devices such as batteries or fuel-cells. A microgrid system is typically capable of operating in “islanded” (off-the grid) or grid-connected mode.
Based on the grid connection "status" of a microgrid, it can be categorized as:
- Permanently Islanded Microgrid. Permanently Islanded microgrid networks are stand alone networks that must produce all of the generation locally that will be consumed by the loads in the network. Islanded microgrid networks are quite often found in remote, northern or island communities where the high cost of importing fuel and the availability of renewable resources (wind, hydro) can make optimization of generation resources very desirable.
- Grid-Tied Microgrid. Grid-tied microgrid networks are able to produce power within its distribution networks as well as import power from a utility source. University campuses and military facilities that have on-site generation for backup power can utilize their on-site generation to offset the costs of electricity when it is cheaper to produce electricity than to buy it.